Describe the Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Using Hb
Terms in this set 127 the transport of O2 between the lungs and the cells of the body is a function of what organ. When carbon dioxide clings to hemoglobin it forms carbanimohemoglobin.

Gas Exchange Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Instead carbon dioxide binds amino acid moieties on the globin portions of hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin which forms when hemoglobin and carbon dioxide bind.
. Each g Hb can carry how much 02. Internal Respiration Internal respiration - gas exchange between blood and tissue cells. Occurs only in the lungs.
When hemoglobin is not transporting oxygen it tends to. The model accounts for hemoglobin saturation the simultaneous binding of o 2 CO 2H 23-DPG to hemoglobin and temperature. In short the change in partial pressure from the alveoli to the capillaries drives the oxygen into the tissues and the carbon dioxide into the blood from the tissues.
When blood has left the heart and is sent to the lungs the concentration of carbon dioxide in the deoxygenated blood is greater than the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. About 20 percent of carbon dioxide is bound by hemoglobin and is transported to the lungs. TF the diffusion of oxygen from alveoli to blood occurs down an average partial pressure gradient of approximately 110 mmHg 150 40 TF the diffusion gradient for oxygen is greater in basal alveoli compared with apical.
Hemoglobin is made up of four symmetrical subunits and four heme groups. When reduced hemoglobin Hb is completely converted to oxyhemoglobin Hb O2 the hemoglobin is said to be fully saturated. Oxyhemoglobin blood aerobic respiration lymph anaerobic respiration nitrogen alveoll carbonic anhydrase carbon dioxide bicarbonate carbonic acid bronchiole Although gas exchange is a continuous process the mechanisms used to transport oxygen.
Describe the structure and function of hemoglobin in gas exchange. As a result the gases in the blood and the lungs move. Because carbon dioxide is released from the lungs blood that leaves the lungs and reaches body tissues has a lower partial pressure of carbon dioxide than is found in the tissues.
Bound to haemoglobin 985. Who are the experts. It converts oxygenated blood into deoxygenated blood.
To investigate the binding and buffering effects a model of blood-tissue gas exchange is used. The partial pressures of carbon dioxide and oxygen as well as the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin influence how readily hemoglobin binds carbon dioxide. The binding and buffering of O 2 and CO 2 in the blood influence their exchange in lung and tissues and their transport through the circulation.
02 bound to Hb 134 mL 02 x 15 g Hb 201 vol 02. This exchange happens through the process of diffusion. In the lungs where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane and at the tissues where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up.
Carbon dioxide does not bind to iron as oxygen does. December 10 2018 vallecula. Explain the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve factors that shift the curve and the effect of these shifts on oxygen uptake and oxygen delivery.
Two alpha subunits. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. What are the two forms O2 is carried in the blood.
TF oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged on a 11 basis across the alveolar-capillary membrane. Oxygen is carried in the blood in two form. It is the iron in hemoglobin that gives blood its red color.
Transport of oxygen- The oxygen is being carried by the. Complete the following paragraph to describe how hemoglobin is involved in gas exchange. Describe the exchange of oxygen carbon dioxide in internal external respirations External respiration or pulmonary gas exchangeis the diffusion of O2 from air in the alveoli of the lungs to blood in pulmonary capillaries and the diffusion of CO2 in the opposite direction.
When hemoglobin consists of a mixture of Hb and HbO2 it is partially saturated. Iron associated with the heme binds oxygen. 134 mL of 02 per g.
1 as dissolved O2 in the blood plasma. Dissolved in the blood 15. External RESP in the lungs converts Deoxygenated blood coming from the right side.
The heart and the blood. About 20 percent of carbon dioxide is bound by hemoglobin and is transported to the lungs. Oxygen is transported in the blood in two ways.
Once oxygen has entered the blood from the lungs it is taken up by haemoglobin Hb in the red blood cells. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Hormone erythropoietin EPO 6.
Haemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that is comprised of four subunits. Describe the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the alveolarcapillary membrane. With each breath carbon dioxide leaves the alveoli and is replaced with oxygen.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body. Instead carbon dioxide binds amino acid moieties on the globin portions of hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin which forms when hemoglobin and carbon dioxide bind.
When hemoglobin is not transporting oxygen it tends to. If Hb level is 15 g percent and if Hb is fully saturated apprx 201 vol of 02 will be bound to Hb. While oxygen binds to the iron content in the heme of hemoglobin carbon dioxide can bind to the amino acid chains on hemoglobin.
Similar to the transport of oxygen by heme the binding and dissociation of carbon dioxide to and from hemoglobin is dependent on the partial pressure of carbon dioxide. The percent saturation of hemoglobin expresses the average saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen. An intermediate amount of carbon dioxide binds directly to hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin.
As dissolved oxygen in the blood plasma. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveolar ducts and pulmonary capillaries occurs through passive diffusion which in relation with the two laws the Daltons law and Henrys law. During internal respiration O 2 and CO 2 diffuse down their partial pressure gradients.
Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood as well as the structure and function of hemoglobin. According to the Daltons law the partial pressure determines the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and lungs lungs and blood. Chemically bound to the hemoglobin that is in the erythrocytes or red blood cells RBCs 4.
The partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide change as blood moves through the body. About 10 of carbon dioxide in the human body is transported this way. These studies among others sparked investigations tions.
Carbon dioxide then diffuses out of the erythrocyte and across the respiratory membrane into the air. The protein inside red blood cells a that carries oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide to the lungs is hemoglobin b. What needs to be added to determine amount of 02 in 100 mL of blood.
Carbon dioxide does not bind to iron as oxygen does. Into the interaction between oxygen and carbon dioxide trans- Because Hb-oxygenation releases protons and HCO- de- port in the blood of vertebrates which continues to the pres- hydration consumes protons there is an extensive interaction ent unabated.

Gas Exchange Anatomy And Physiology Ii

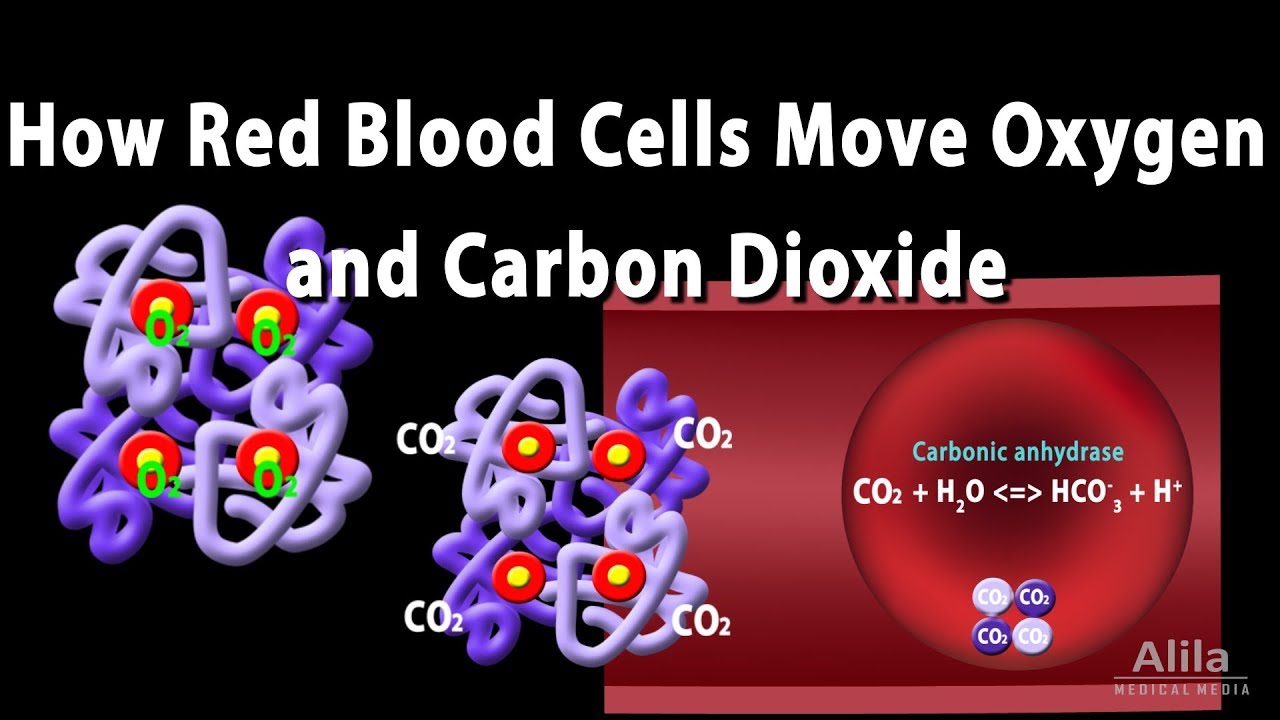
How Red Blood Cell Carry Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide Animation Youtube

No comments for "Describe the Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Using Hb"
Post a Comment